Top financial technologies that is changing the payment system
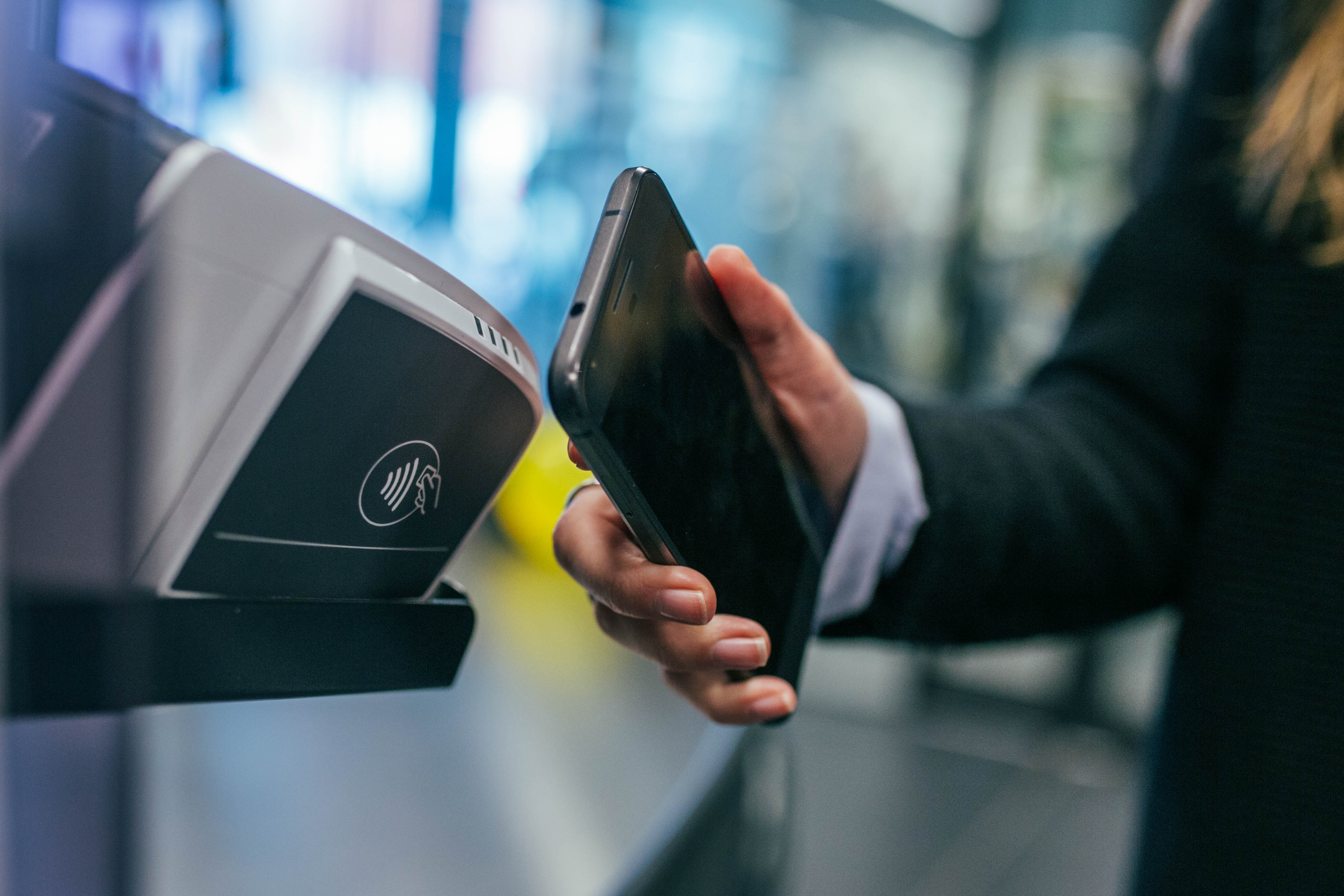

Advances in payment technologies have dramatically disrupted the finance industry and traditional brick-and-mortar stores. Payment transactions have evolved considerably from simple cash payments to bank cards and are now transforming again to encompass contactless capabilities. This new digitally-driven era has seen developments such as near-field communication technology (NFC), mPOS and wearables become the norm.
With the advancement of the aforementioned technologies, businesses will need to adapt to ensure relevancy in the digital age. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global digital payments market is set to be worth $86.76bn by 2023, an increase from $38bn in 2018.
Ahead of Innovation Enterprise’s Payments Innovation Summit in San Francisco at the end of November, we look at how the development of NFC technology, mPOS terminals and mobile wallets have disrupted payment processes.
NFC technology is connecting businesses and consumers
NFC technology’s first patent dates back to 1983 and was finally developed in 2002 by Sony and Phillips. However, it only gained popularity in recent years in response to the demand for IoT-enabled technology to streamline and accelerate payment processes.
NFC tech allows for a secure two-way exchange between electronic devices. The technology enables “consumers to perform contactless transactions, access digital content and connect electronic devices with a single tap”, according to the NFC Forum.
Key vendors within the NFC global market include Apple, Google, Mastercard, Paypal, Samsung, Visa – all offering contactless digital wallet/mobile payment solutions.
A MarketsandMarkets report found that the overall global market of NFC technology is forecast to reach $21.84bn by 2020, growing at a CAGR of 17.1% between 2015–20. The key drivers behind the growth is said to be the increased demand for cashless transactions, adoption of smart devices and the increasing adoption of e-commerce.
Wearable devices increasingly transforming contactless payment processes
IoT pioneers have been innovating across a diverse range of sectors and the payment industry has not gone unnoticed with wearables among the most significant developments emerging from IoT.
The wearables concept first came to motion in the 1990s with portable computing, but it was pioneered by the Fitbit in 2009, before Pebble technology spearheaded the first commercially available smartwatch in 2012. It paved the way for the development of smartwatches by software moguls Apple and Google.
According to a report by global consultancy firm Capgemini, the number of payments made via wearables is expected to rise and is forecast to form 30% of the wearable device market by 2020.
The key drivers of wearables as a payment device include the increased processing power in smart devices, smartphones and tablets. Also fueling the wearables market has been the general availability of high-speed internet, the increased focus on IoT-enabled payments (IoP) and increased demand for a seamless banking experience, driving banks to develop digitally-driven solutions with enhanced security features such as biometrics and cryptography.
A report by ResearchandMarkets suggested that the key players in the market driving the adoption and development of the tech include the Alibaba Group, Apple Pay, Google Pay and Mastercard.
Conversely, factors hindering the adoption of NFC technology, as discovered in a report by Capgemini, include cyber threats and payment-associated fraud which have been on the rise due to the increasing adoption of mobile payments and wearables devices. Furthermore, the report stated that in 2016, card fraud accounted for more than $24m in losses and predicted that cyber-attacks could cost businesses more than $2 trillion by 2019.
mPOS is transforming business performance
The advancements of NFC technology and wearable devices have also accelerated technology developments of the traditional cash register and resulted in the exponential growth of the mPOS market.
mPOS is defined as a portable, mobile, point of sale (POS) which works as a payment register via a smartphone or tablet. US mPOS terminal supplier Square was the first to develop an mPOS solution, Square Reader, and disrupt the payment space in 2009. The device enabled micro-merchants who previously were not able to process card payments. Research and advisory firm Mercator Advisory Group noted that the emergence of Square as a mPOS provider was a game-changer due to key attributes such as the acceptance of the technology, ease of transaction processes and cost efficiency.
The mPOS market is now projected to be worth more than $55bn by 2024, according to Global Market Insights.
Indian-based mobile solutions provider Mahindra Comviva outlined that mPOS terminals have propelled the traditional card-based payments to cloud-based services.
“The use of mobile devices in stores means that staff can roam the aisles and engage proactively with shoppers,” Mahindra Comviva stated. “They can better respond to queries, look up product details on their devices, exploit the immediacy of the payment function if the customers decide to buy and potentially provide instant offers, discounts or loyalty-based promotions.”
However, vendors need to ensure security of the mPOS systems by assuring PCI compliancy to accept encrypted payments from chip cards or NFC-based payments such as Apple Pay or Google Pay.
To find out more about the payments industry trends and strategy visit Innovation Enterprise’s Payments Innovation Summit in San Francisco on November 28–29, 2018. See the full agenda and by tickets HERE.

















Facebook Comments